User Guide
So I have this running, now what?
Cheat Sheet
### Sequencing
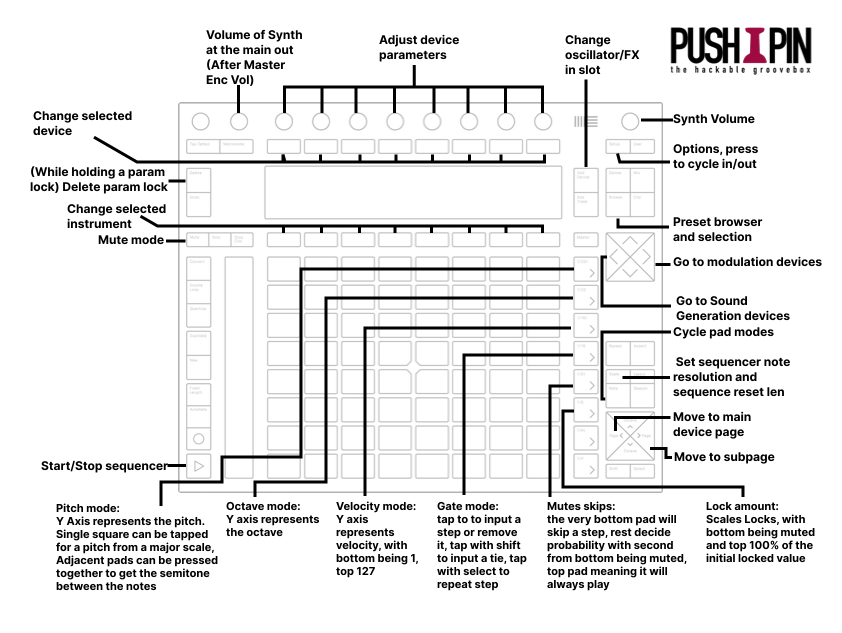
Press the NOTE button to activate the sequencer. The Push 2 “tempo” buttons (directly right of the pads) activate different sequencer modes:
- 1/32t Pitch mode: Y Axis represents the pitch. Single square can be tapped for a pitch from a major scale, adjacent pads can be pressed together to get the semitone between the notes.
- 1/32 Octave mode: Y axis represents the octave.
- 1/16t Velocity mode: Y axis represents velocity, with bottom being 1, top 127
- 1/16 Gate mode: tap to to input a step or remove it, tap with SHIFT to input a tie, tap with SELECT to repeat step
- 1/8t Mute skip: the very bottom pad will skip a step, the rest decide probability with second from bottom being muted; top pad meaning it will always play.
- 1/8 Lock amount: Scales Locks, with bottom being muted and top 100% of the initial locked value
It’s good to start on “Gate mode”, add a bunch of steps, and then refine those in pitch mode.
### Routing with Overbridge
For Developers
To hack on top of Pushpin, it helps to understand what it’s doing upon boot because it interacts with several different subsystems.
The Pushpin Linux distribution spawns 8 duplex Pipewire interfaces, each with 16 inputs and outputs. These are loaded on boot using the Pipewire config located in /home/pushpin/.config/pipewire/pipewire.conf.d/pushpin_groovebox.conf (which is also a good place to put any bespoke Pipewire changes). Another duplex for controlling instrument volumes is also initialised as pushpin-volumes. The pushpin-n duplex devices are dynamically connected to using the audio-in device in Pushpin and are used to manage track audio inputs, enabling complex routing.
Once the system has booted, it logs into the user pushpin (default password: pushpin) and runs /home/pushpin/start_pushpin.sh, which is ultimately an alias for /home/pushpin/s/music_devices/pushpin_groovebox/run.sh. This starts Python running /home/pushpin/s/music_devices/pushpin_groovebox/app.py, the main entry point for the codebase.
Pushpin starts by instantiating eight instances of surge-xt-cli, the command-line version of the Surge XT softsynth. It waits for these to load and then spawns overwitch, an open source Overbridge client, and waits for it to load.
It then disconnects the Surge instances from the default audio device and connects them to pushpin-volumes.
Please see app.py for a full sense of what Pushpin initialisation looks like. Also, try running qpwgraph in Wayland to see how the connection pathways work (run wayland-pi at the command line to load Wayland).